Vagina
Vagina
Define Vagina : The vagina is a fibromusculo-membranous sheath communicating the uterine cavity with the exterior at the vulva.
We have described:
Anatomy of Vagina
Blood supply of Vagina
Nerve supply of Vagina
Describe the changes in the vaginal epithelium at different ages?
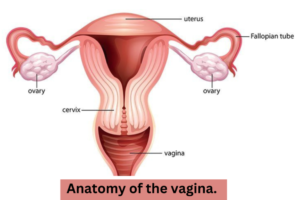
Anatomy of the Vagina :
Direction: The canal is directed upwards and backwards forming an angle of 45 degree with the horizontal in erect posture.
Diameter :About 2.5cm being widest in the upper parts and narrowest at its introitus.
Walls: An anterior posterior and two lateral walls. The length of the anterior wall is about 7cm and that of the posterior wall is about 9 cm.
Relations:
- Anterior: The upper one -Third is related with the pouch of Douglas, the middle-thirds are with the urethra.
- Posterior : The Upper one-Third is related with the pouch of Douglas, The middle-Third with the anterior rectal wall separated by retrovaginal septum and the lower-third is separated from the canal by the perineal body.
- Lateral walls: The upper one-third is related with pelvic cellular tissue at the base of broas ligament and which the ureter and the uterine artery lie approximately 2 cm from the lateral fornices. The middle – Third is blended with the levator ani and the lower- third is related with the bulbocavernous muscles, vestibular bulbs and Bartholin’s glands.
Structures: Layers from within outwards are
- Mucous Coat.
- Submucosa layer.
- Muscular Layer
- Fibrous coat derived from the endopelvic fascia and is highly vascular.
Blood supply of Vagina
Arterial supply:
- Cervicovaginal branch of the uterine artery.
- vaginal artery a branch of anterior division of internal iliac or in common origin with the uterine artery.
- Middle rectal artery.
- Internal pudendal artery.
Venous drainage : Drain into internal iliac veins and internal pudendal veins.
Nerve supply of Vagina
- Sympathetic and parasympathetic from the pelvic plexus.
- The lower part is supplies by the pudendal nerve.
Changes in the vaginal epithelium at different ages:
Newbron: The vagina of the newborn is under the influences of oestrogen which has crossed the placenta from maternal circulation.
Puberty:
- The epithelium is moderately well developed well and contains glycogen.
- Lactobacilli appear on the 3rd or 4th day when the vaginal acidity approaches that of an adult.
- By the 10-14 days the oestrogen stimulus is lost and the epithelium atrophies and becomes devoid of glycogen.
- the pH then rises to approximately 7 and remains at the level unit the approach of the puberty.
- Lacltobacilli are predominant organism after puberty.
Pregnancy: During pregnancy the amount of glycogen is increased to a maximum and the acidity of the vagina is high.
Menopause: After the menopause the epithelium atrophies and losses the glycogen. Lactobacilli are found in fewer numbers and the pH rise to range of 6-8.

I keep listening to the rumor talk about receiving free online grant applications so I have been looking around for the best site to get one. Could you tell me please, where could i acquire some?
Heya i’m for the first time here. I found this board and I find It really helpful & it helped me out a lot. I hope to offer one thing back and help others such as you aided me.
I’ve been absent for a while, but now I remember why I used to love this blog. Thanks , I will try and check back more often. How frequently you update your web site?
It’s really a cool and useful piece of info. I am happy that you simply shared this helpful info with us. Please keep us informed like this. Thank you for sharing.