Sinusitis : Acute sinusitis & chronic sinusitis
Sinusitis
We have described in article :
Definition of sinusitis
Classification of rhinosinusitis
Management of acute sinusitis
Management of chronic sinusitis
Complications of sinusitis
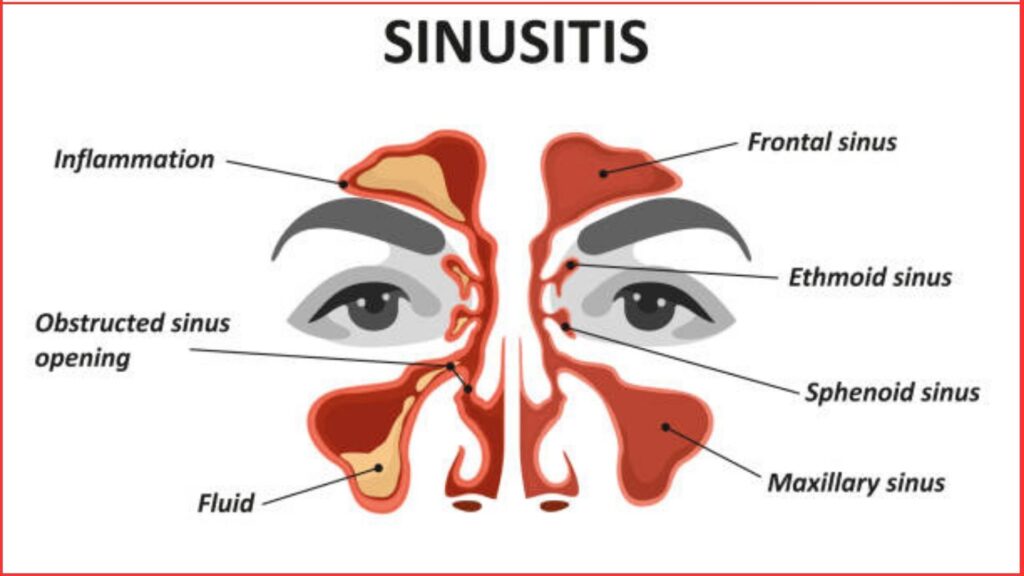
Definition of sinusitis :
Sinusitis : It is an inflammation of the mucosa of any or all of the paranasal air sinuses. However, as this condition is invariably associated with inflammation of the nasal mucosa, hence the term rhinosinusitis (RS) has been preferred.
Classification of rhinosinusitis :
Rhinosinusitis Task Force (2007) gave the clinical classification as
- Acute rhinosinusitis : Symptoms lasting for less than 4 weeks with complete resolution.
- Subacute rhinosinusitis : Duration 4-12 weeks
- Chronic rhinosinusitis : Duration 12 weeks.
- Recurrent rhinosinusitis : Four or more episodes of RS per year, each lasting for 7-10 days or more with complete resolution in between the episodes.
ACUTE SINUSITIS
Definition of acute sinusitis :
Acute sinusitis: It is an acute inflammation of the mucosa of any or all of the paranasal air sinuses.
- It is common in-Maxillary> Ethmoidal > Frontal >Sphenoidal sinuses.
- If all the sinuses are involved, then it is called pansinusitis.
Organisms responsible for acute maxillary sinusitis :
Viruses :
- Rhino virus
- Influenza & para influenza viruses.
Bacteria :
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Haemophilus influenzae
- Moraxella catarrhalis
- Streptococcia pyogens
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Klebsiella pneumoniae.
Management of acute maxillary sinusitis:
Clinical features:
1). Constitutional symptoms :
- Fever
- General malaise.
- Body ache.
2) Headache.
3) Pain:
- Typically, it is situated over the upper jaw, but may be referred to the gums or teeth.
- Pain is aggravated by stooping coughing or chewing.
- Occasionally, pain is referred to the ipsilateral supraorbital region and thus may simulate frontal sinus infection.
4) Tenderness: Pressure or tapping over the anterior wall of antrum produces pain.
5) Redness and oedema of cheek
6) Nasal discharge.
7) Postnasal discharge.
Investigation of acute sinusitis :
- Transillumination test.
- X-ray PNS Waters’ view, show either an opacity or a fluid level in the involved sinus.
- Computed tomography (CT) scan.
- Nasal swab culture & drug sensitivity.
- Pus for culture and sensitivity.
Treatment of acute sinusitis :
Medical treatment :
- Antimicrobial drugs :
.Ampicillin and amoxicillin are quite effective
.Erythromycin or doxycycline or cotrimoxazole are equally effective.
- Nasal decongestant drops : To prevent blocking of osteum. Oxymetazoline HCI: At least 4 drops in each nostril 3 times daily for 10-15 days.
- Steam inhalation.
- Analgesics : Paracetamol or any other suitable analgesic.
- Anti-histamine: Chlorpheniramine maleate-4mg 8 hourly.
- Hot fomentation.
Surgical treatment : If medical treatment fails: Antral lavage.
Radiological tests to investigate the paranasal sinuses :
- X-ray PNS Waters’ view: show either an opacity or a fluid level in the involved sinus.
- Computed tomography (CT) scan.
Three standard X-ray views of paranasal sinuses :
- Occipito mental (OM) view (Waters’ view).
- Occipitofrontal view/nose-forehead position. (Caldwell’s view).
- Lateral view.
- Submentovertical (basal) view.
- Right & left oblique view.
Complications of maxillary sinusitis :
- Subacute or chronic sinusitis.
- Frontal sinusitis.
- Osteitis or osteomyelitis of the maxilla.
- Orbital cellulitis or abscess.
Chronic sinusitis
Definition : It is a chronic inflammatory disease of nasal and paranasal sinus mucosa where symptomatology has continued beyond 12 weeks.
- Sometimes there are acute exacerbations superimposed on chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS), where symptoms worsen but return to baseline of CRS after treatment.
Common bacteria responsible for chronic maxillary sinusitis :
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Escherichia coli.
Management of chronic maxillary sinusitis :
Symptoms of chronic sinusitis :
- Nasal obstruction.
- Nasal or postnasal purulent discharge
- Facial pain and pressure, and
- Disturbance of smell (hyposmia or anosmia).
Signs of chronic sinusitis : Endoscopic examination of nose may reveal –
- Oedema of nasal mucosa in the anterior or posterior
- Purulent discharge.
Investigation of chronic maxillary sinusitis :
- X-ray PNS occipitomental (OM) view 2).
- Pus for C/S.
- Coronal CT scan of paranasal sinuses.
- MRI.
- Proof puncture
- Sinus endoscopy.
Treatment of chronic maxillary sinusitis :
Medical treatment : (not satisfactory)
- Antibiotics Broad-spectrum antibiotics should be chosen based on the culture and sensitivity of discharge from the middle meatus.
- Saline irrigations
- Topical decongestants.
- Steroid sprays
- Anti-allergy treatment : Antihistamines and leukotriene receptor antagonists (such as montelukast).
Surgical treatment :
- Endoscopic sinus surgery. Functional endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS)
- Other surgical techniques :
- Antral puncture and irrigation.
- Intranasal antrostomy
- Caldwell-Luc operation.
Radiological findings of chronic maxillary sinusitis in an X-ray PNS OM view:
- Mucosal thickening of the lining mucosa.
- Opacity or uniform haziness of the maxillary sinus.
- Polypoid hypertrophy of the lining mucosa.
- Fluid level.
- Osteitis or osteoclerosis.
Complications of chronic maxillary sinusitis :
- Pharyngitis.
- Laryngitis.
- Otitis media.
- Mucocele of maxilla.
- Orbital complications: Orbital cellulitis, Orbital abscess.
- Intracranial complications: Meningitis, Brain abscess, Cavernous sinus thrombosis.
- Osteomyelitis in maxilla (in children).
Complications of sinusitis :
Local :
- Mucocele / Mucopyocele.
- Mucous retention cyst.
- Osteomyelitis : Frontal bone (more common), Maxilla
Orbital :
- Preseptal inflammatory oedema of lids.
- Subperiosteal abscess.
- Orbital cellulitis.
- Orbital abscess.
- Superior orbital fissure syndrome.
- Orbital apex syndrome.
Intracranial :
- Meningitis.
- Extradural abscess.
- Subdural abscess.
- Brain abscess.
- Cavernous sinus thrombosis.
Descending infection :
- Otitis media.
- Pharyngitis and tonsillitis.
- Persistent laryngitis and tracheobronchitis.
Focal infections :
- Polyarthritis.
- Tenosynovitis.
- Fibrositis.
- Certain skin diseases.
